Ohm Resistors (Ω)
Non-returnable
Rs.5.00
Ohm resistors (Ω) are fundamental electronic components used to control and limit the flow of electrical current in a circuit. They are named after Georg Simon Ohm, a German physicist who formulated Ohm's law, which relates voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits.
Choose the below Ohms Resistor Values (Pack of 5pcs):
Values
Choose Quantity
Product Details
Ohm resistors are characterized by their resistance value, which is measured in ohms (Ω). Here are some key points about Ohm resistors:
1. Resistance Value: The primary characteristic of an Ohm resistor is its resistance value, which is specified in ohms (Ω). Resistance represents the opposition to the flow of electrical current and determines how much current will flow through the resistor when a voltage is applied.
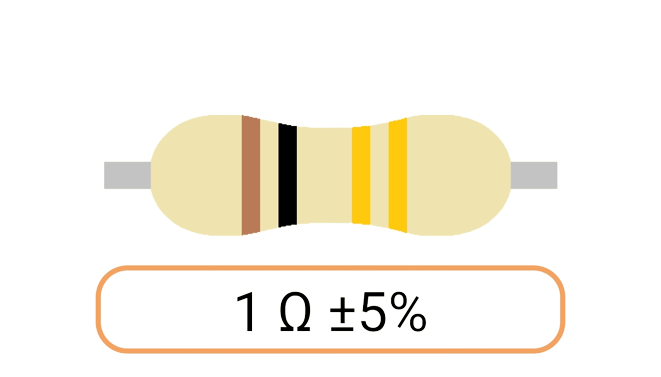
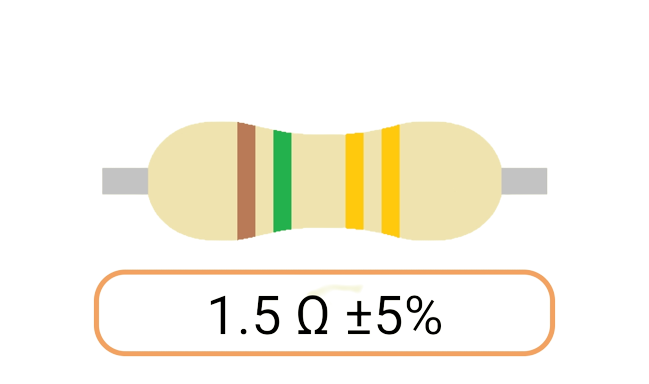
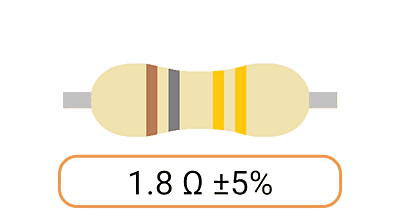
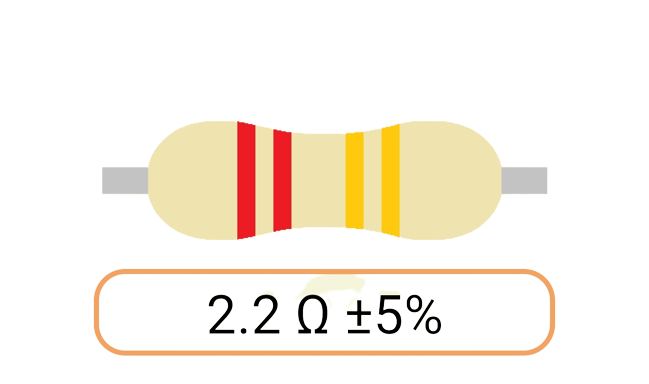
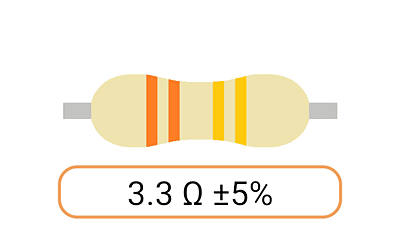
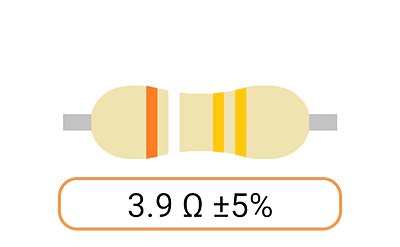
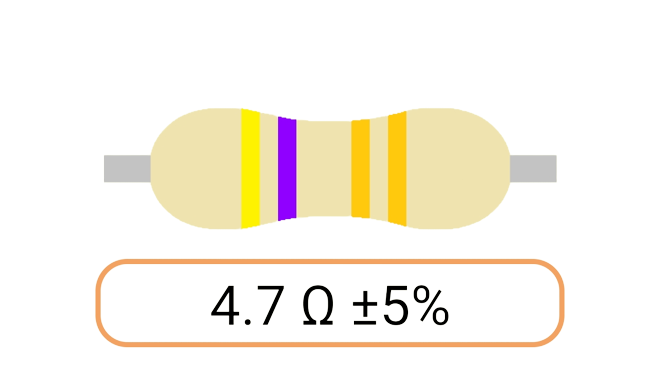
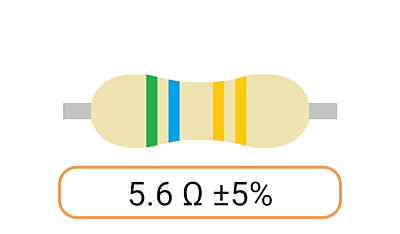
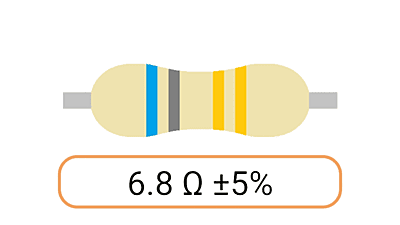
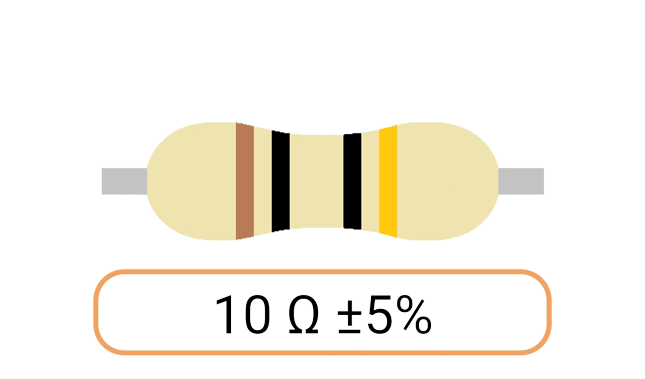
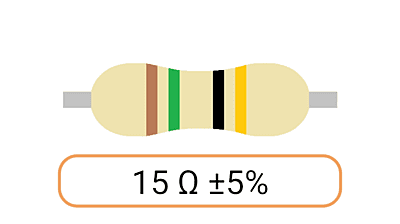
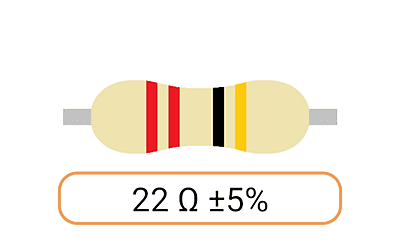
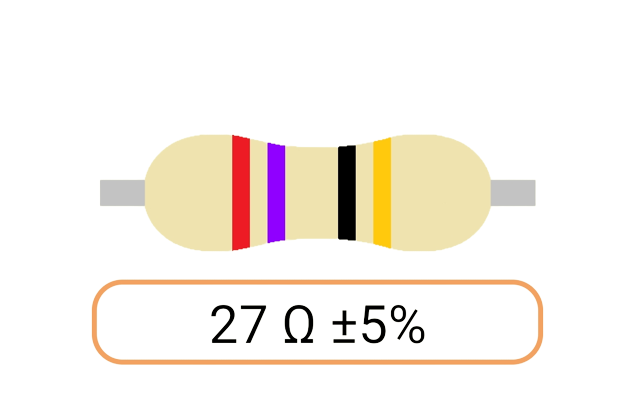
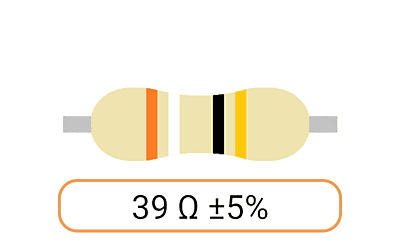
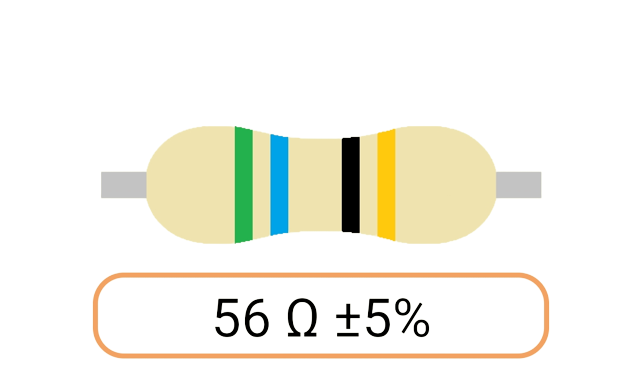
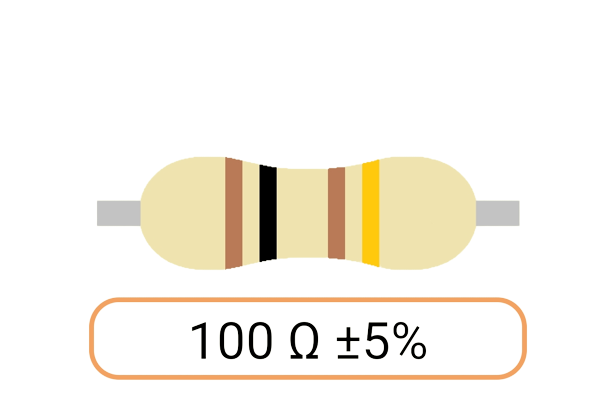
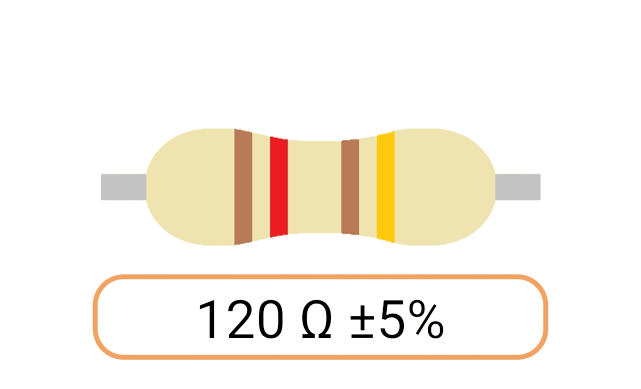
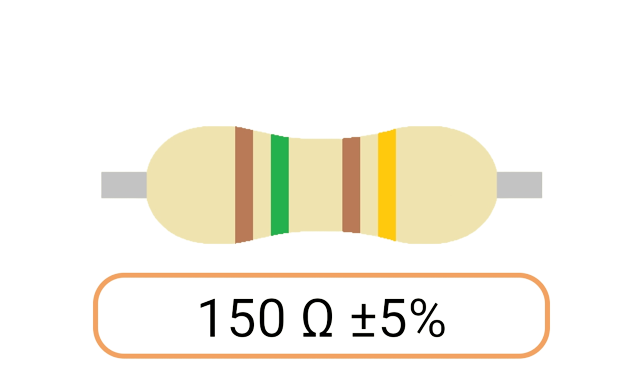
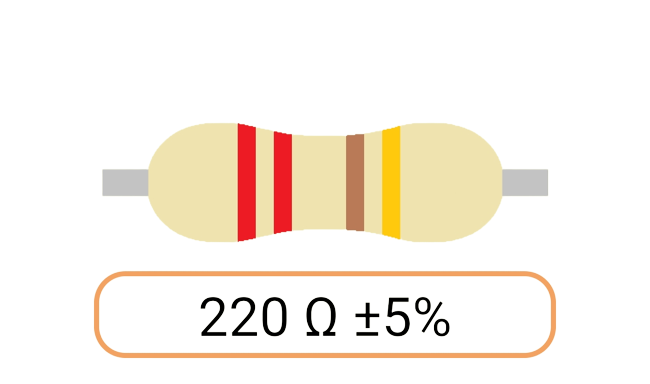
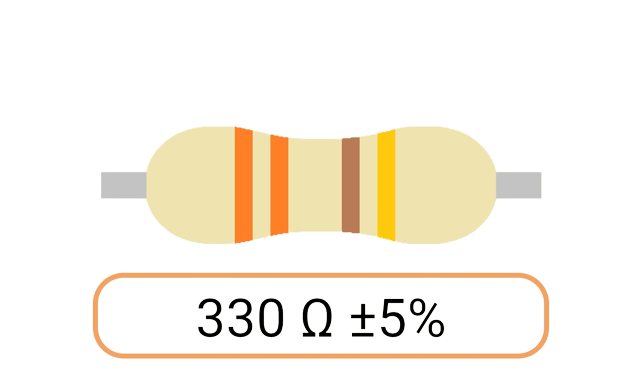
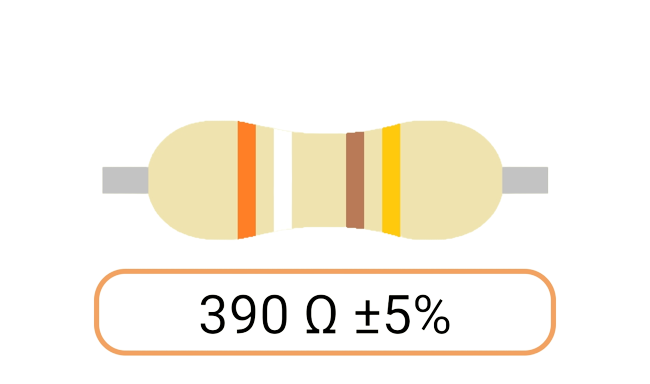
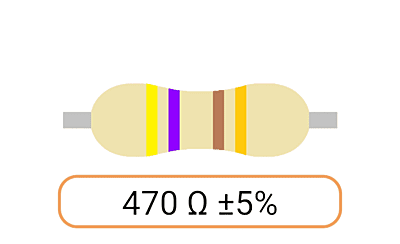
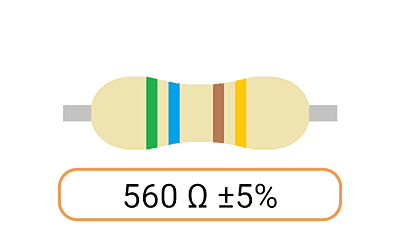
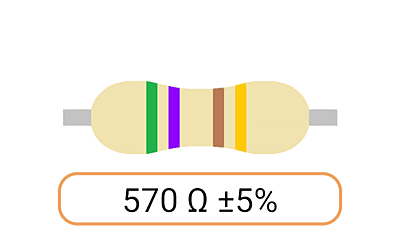
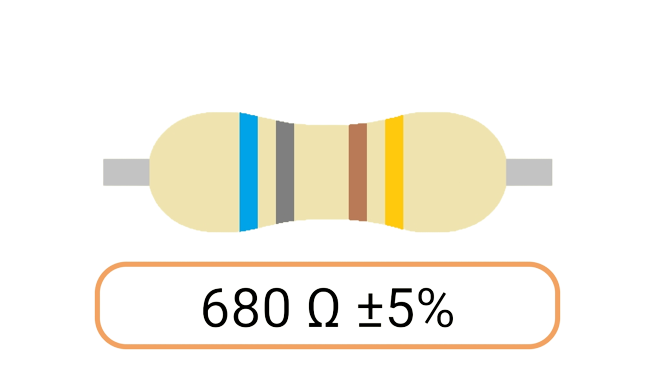
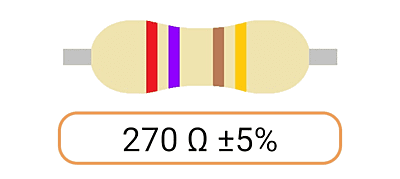
2. Color Coding: Most Ohm resistors have color bands or stripes printed on their bodies to indicate their resistance value and tolerance. The color code is a standardized system that allows you to easily identify the resistance value and tolerance of a resistor. Each color represents a digit, and the combination of colors provides the resistor's value.
3. Tolerance: The tolerance of an Ohm resistor is a measure of how close its actual resistance can be to the specified value. Common tolerance values include 1%, 5%, and 10%. A 1% tolerance resistor, for example, means that its resistance can deviate by up to 1% from the specified value.
4. Power Rating: Ohm resistors also have a power rating, typically measured in watts (W). The power rating indicates the maximum amount of electrical power the resistor can dissipate without overheating or being damaged. It's important to select a resistor with an appropriate power rating for the application to avoid overheating and failure.
5. Types: Ohm resistors come in various types, including:
Carbon Film Resistors: These are made by depositing a carbon film on a ceramic substrate. They are inexpensive and suitable for general-purpose applications.
Metal Film Resistors: Metal film resistors are made by depositing a thin metal film (usually nickel-chromium) on a ceramic substrate. They offer better stability and precision compared to carbon film resistors and are commonly used in precision circuits.
Wirewound Resistors: Wirewound resistors are made by winding a resistive wire (often nichrome) around a ceramic or fiberglass core. They provide high power-handling capabilities and are used in high-power applications.
6. Applications: Ohm resistors are used in countless electronic circuits and applications, including voltage dividers, current limiting, signal conditioning, filter circuits, voltage regulation, and many others.
7. Symbols: In circuit diagrams and schematics, resistors are typically represented by the symbol Ω, which signifies resistance in ohms.
8. Resistance Calculations: Ohm's law (V = I * R) can be used to calculate the resistance (R) of a resistor when the voltage (V) across it and the current (I) passing through it are known. Rearranging the formula, you can calculate current or voltage given resistance and the other known values.
