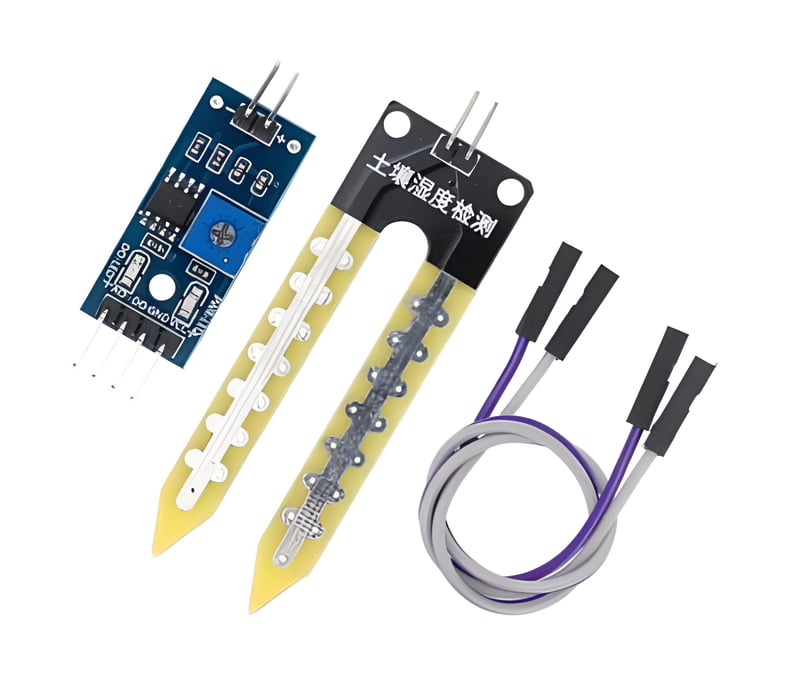

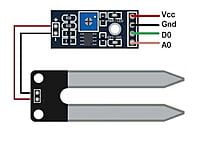
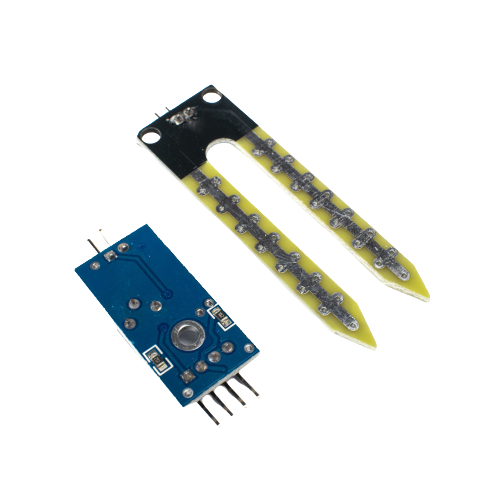

Soil Moisture Sensor
Product Details
Measurement Principle: Soil moisture sensors typically operate on one of the following principles:
- Resistance-based: These sensors measure the electrical resistance between two or more probes inserted into the soil. As soil moisture increases, its electrical conductivity changes, which is used to estimate moisture content.
- Capacitance-based: These sensors measure the soil's dielectric permittivity, which varies with moisture content. They typically have two electrodes or plates separated by a dielectric material (the soil).
Analog or Digital Output: Soil moisture sensors can provide analog or digital output signals.
- Analog: Analog sensors provide a continuous voltage or current output that correlates with soil moisture levels. This output must be read and interpreted by a microcontroller or data logger.
- Digital: Digital sensors provide binary data (e.g., wet/dry) or a digital representation of soil moisture levels. They may have built-in ADCs (Analog-to-Digital Converters) and communicate through digital protocols like I2C or UART.
Calibration: Many soil moisture sensors require calibration to provide accurate moisture readings. Calibration involves determining the sensor's response to different moisture levels in a controlled environment.
Installation: To use a soil moisture sensor, it must be properly inserted into the soil. The sensor's probes or electrodes should be placed at the desired depth, usually in the root zone of the plants being monitored.
Applications:
- Agriculture: Farmers use soil moisture sensors to optimize irrigation, prevent overwatering, and conserve water resources.
- Gardening: Gardeners can use these sensors to determine when and how much to water their plants.
- Environmental Monitoring: Soil moisture data is valuable for environmental studies, especially in arid or drought-prone regions.
- Research: Scientists use soil moisture sensors in various research applications, including ecology and hydrology.
Data Logging: In many applications, data from soil moisture sensors is logged over time to track changes in soil moisture levels and make informed decisions about irrigation or other interventions.
Maintenance: Soil moisture sensors require occasional maintenance, including cleaning and calibration, to ensure accurate readings.


