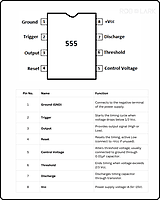
Operational Modes: The NE555 can operate in various modes, including astable (oscillator), monostable (one-shot), and bistable (flip-flop) modes. Each mode serves a different purpose.
Astable Mode: In astable mode, the 555 timer generates a continuous square wave output. It's commonly used for applications like LED flashers, tone generators, and clock circuits.
Monostable Mode: In monostable mode, the 555 timer acts as a one-shot pulse generator. It produces a single pulse when triggered, making it useful for applications like time-delay circuits, debounce circuits, and pulse shaping.
Bistable Mode: In bistable mode, the 555 timer operates as a flip-flop. It has two stable states and can be used for applications like toggling an output, flip-flop control, or building simple digital logic.
Timing Components: To set the timing parameters (frequency and pulse duration), the NE555 timer relies on external resistors and capacitors connected to its pins.
Wide Voltage Range: The NE555 can typically operate over a wide voltage range, making it suitable for both low-voltage and high-voltage applications.
Trigger and Threshold Inputs: The NE555 has two external inputs, Trigger (TRIG) and Threshold (THRES), which are used to control the timing operation.
Output Modes: The NE555 timer can drive both digital and analog loads. Its output can source or sink current, depending on the configuration.
Precision: While the NE555 is a versatile IC, it may not be as precise as dedicated timer ICs. If high precision is required, additional circuitry may be needed.
Applications: The NE555 timer finds applications in electronic projects, from basic LED blinkers to complex timing and control systems.
Datasheet: To use the NE555 effectively, it's essential to consult the datasheet provided by the manufacturer. The datasheet contains detailed information about pin configurations, operating modes, timing equations, and recommended operating conditions.