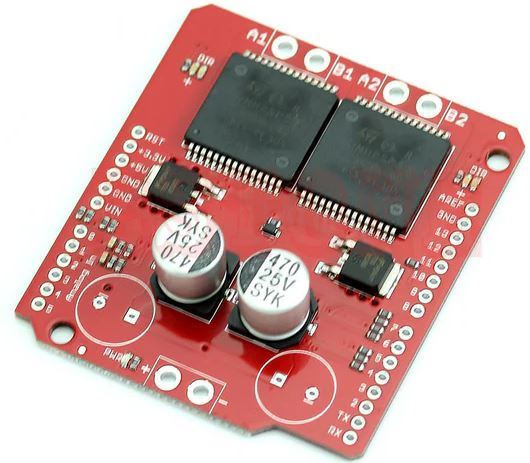
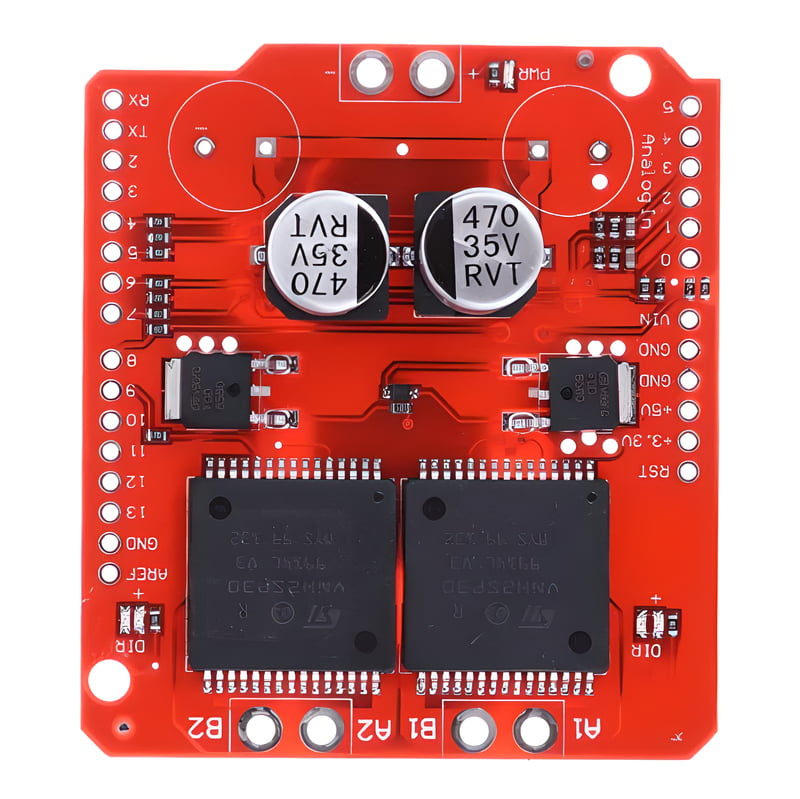

Dual Monster: VNH2SP30 Motor Driver Shield
Product Details
Key Features:-
Dual Motor Control: As the name suggests, this shield is designed to control two motors independently. It can be used to drive two DC motors or control the motion of a stepper motor.
High Current Handling: The shield is capable of handling high currents, making it suitable for driving motors with significant power requirements. The VNH2SP30 motor driver chips used on the shield are rated for a high current capacity.
Bi-Directional Control: It allows you to control the direction of motor rotation, enabling forward and reverse movement for each motor.
PWM Speed Control: The shield supports pulse-width modulation (PWM) for controlling the speed of the motors. By varying the PWM signal, you can adjust the motor speed smoothly.
Current Sensing: Some versions of this shield include current sensing functionality, which can be useful for monitoring the motor's current consumption and detecting stalls or overloads.
Overcurrent Protection: The motor driver chips often come with built-in overcurrent protection, helping prevent damage to the motors or the shield in case of excessive current draw.
Control Interface: It typically connects to a microcontroller or development board (such as Arduino) using standard header pins. This makes it easy to integrate into various projects.
Functionality:
- The shield takes input signals from a microcontroller or development board and translates them into motor control signals.
- It provides a convenient way to control the direction and speed of motors using software commands.
- The shield can be used in various applications, including robotics, remote-controlled vehicles, automation systems, and more.
- It simplifies the motor control process, making it easier to build projects that involve motion or actuation.
Applications:
Hardware Setup: Connect the shield to your microcontroller or development board using the appropriate header pins. Ensure that the power supply voltage matches the voltage requirements of your motors.
Motor Connections: Connect the motors to the motor driver outputs on the shield. Pay attention to the polarity and wiring of the motors.
Software Control: Write a program on your microcontroller to send commands to the shield. This typically involves specifying motor directions, speed, and other control parameters.
Power Supply: Provide the necessary power supply voltage to the shield to ensure that the motors receive adequate power.
Testing and Calibration: Test the motor control functionality and fine-tune the settings as needed to achieve the desired motion or performance.


