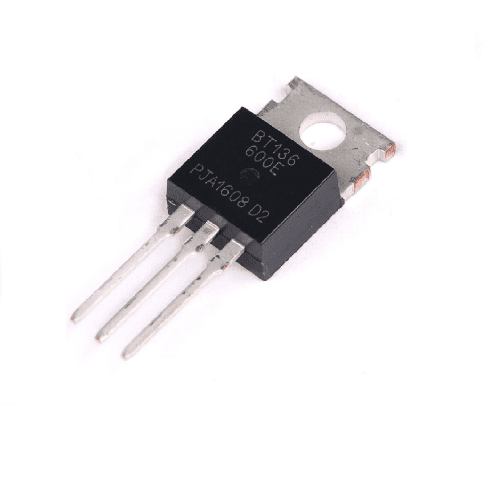
BT136 600D 4 - Amp TRIAC IC
Product Details
TRIAC Function: A TRIAC is a bidirectional semiconductor switch that can control AC power by switching it on and off during different parts of the AC waveform. It is commonly used for applications such as controlling the brightness of incandescent lamps, motor speed control, and AC power switching.
Voltage Rating: The BT136 600D has a maximum voltage rating of 600 volts. This means it can handle AC voltage levels up to 600 volts.
Current Rating: It has a maximum current rating of 4 amps. This indicates the maximum continuous current that can flow through the device without causing damage.
Gate Trigger Current: TRIACs are triggered into conduction by applying a gate current. The BT136 600D typically has a gate trigger current in the range of a few milliamperes (mA). The gate current is usually supplied by a low-voltage control circuit.
Isolation: TRIACs are typically used in AC applications, and electrical isolation is often required between the control circuit and the power circuit. Isolation can be achieved using optocouplers or other isolation devices.
Package Type: The BT136 is available in various package types, with the TO-220 being a common package for medium-power TRIACs like the BT136 600D.
Applications: TRIACs like the BT136 are used in a wide range of applications, including light dimmers, motor speed controllers, heating control systems, and AC power switches.
Heat Sink: Depending on the application and load current, it may be necessary to attach a heat sink to the TRIAC to dissipate heat generated during operation.
Triggering: TRIACs are typically triggered at a specific point in the AC waveform to control the power delivered to a load. Proper synchronization with the AC waveform is essential for reliable operation.


